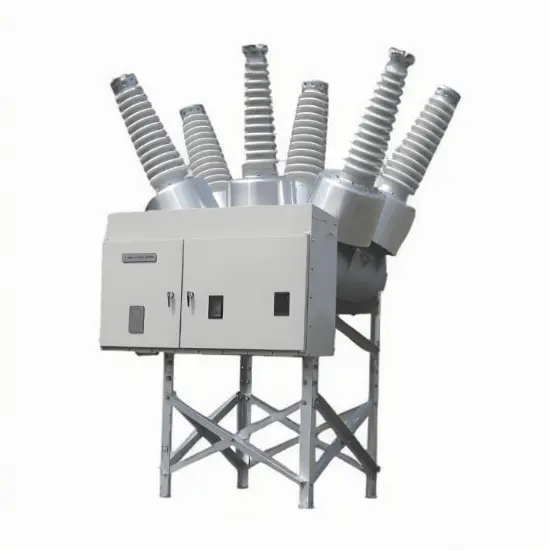
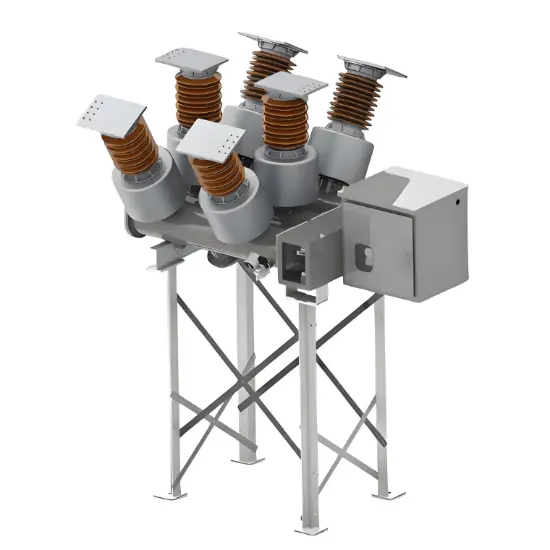
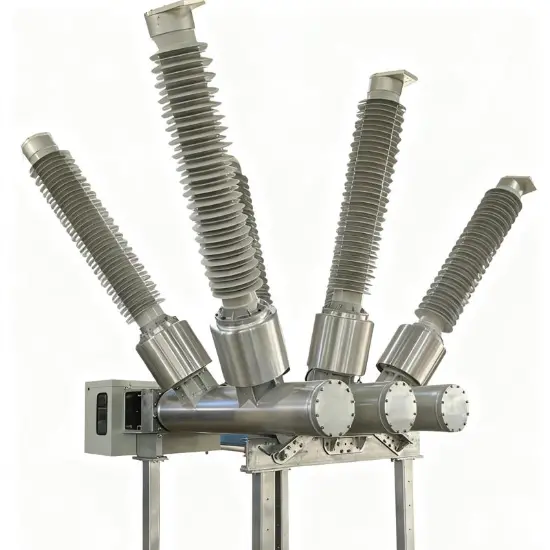
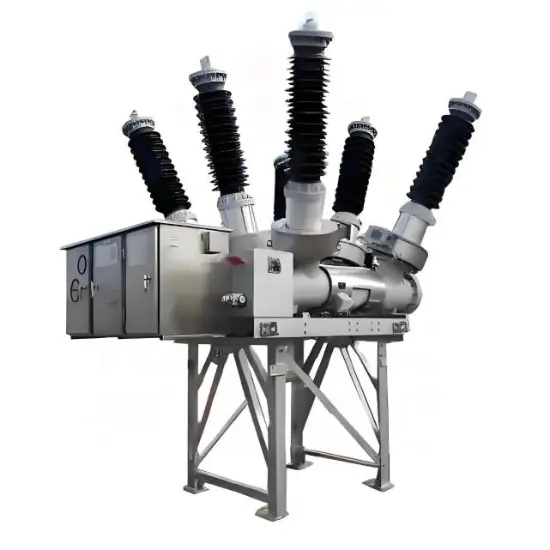
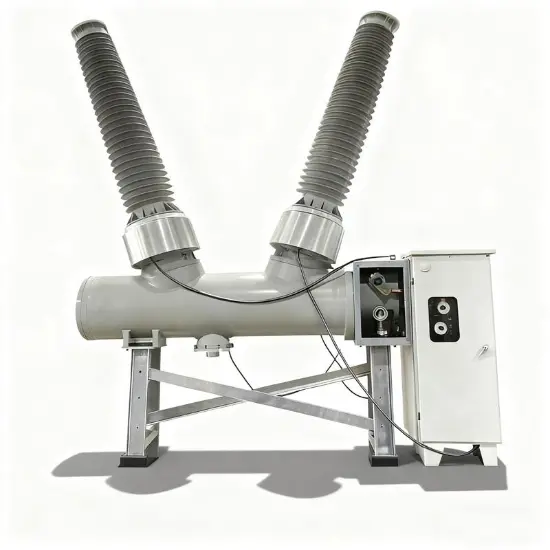
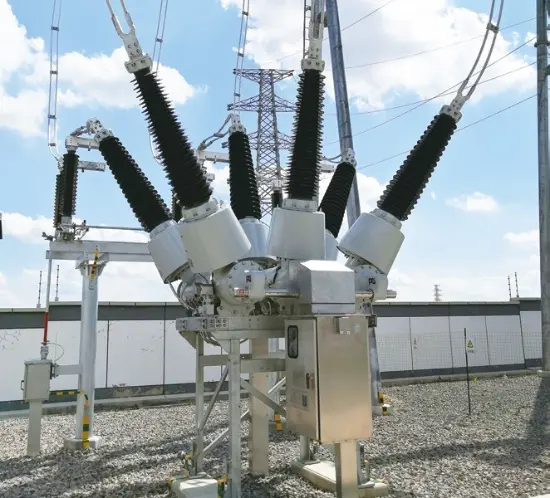
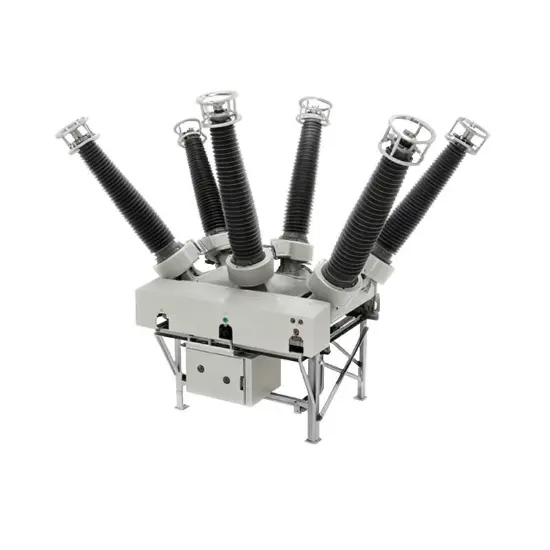
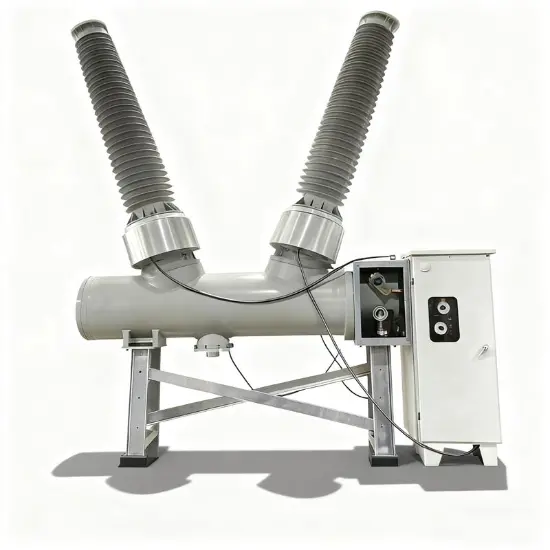
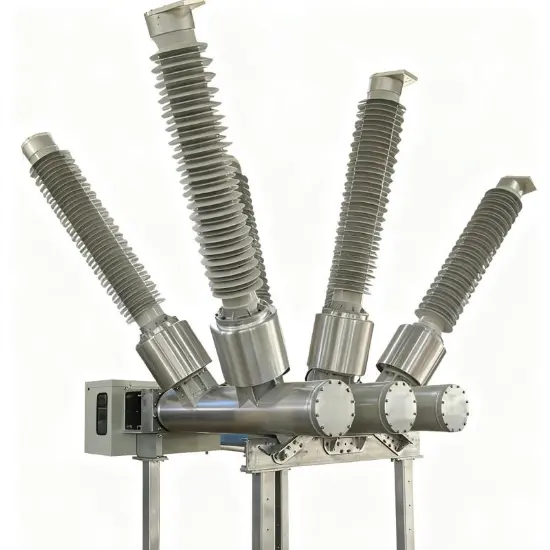
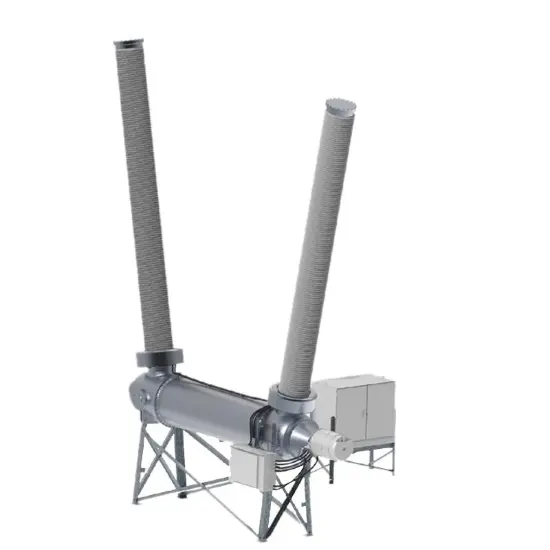
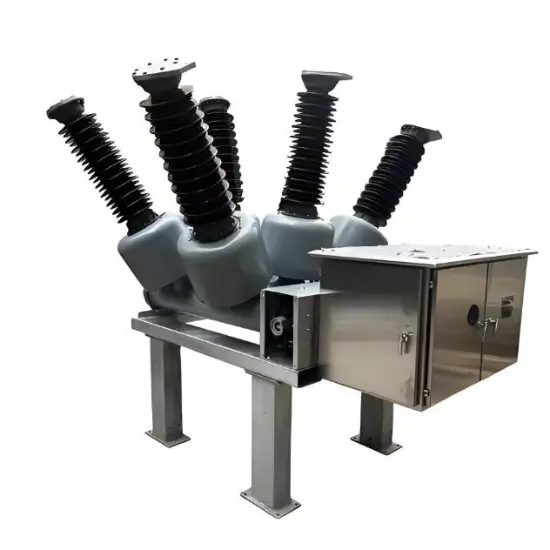
36kV 72.5kV Disjoncteur à vide avec cuve morte isolée à l'air sec
| Marque | ROCKWILL |
| Numéro de modèle | 36kV 72.5kV Dry Air Insulated Dead Tank Vacuum Circuit Breaker(VCB) |
| tension nominale | 72.5kV |
| courant nominal | 2000A |
| fréquence nominale | 50/60Hz |
| Série | NVBOA |
Description
Le disjoncteur de cuve morte à isolation à air sec est né de la technologie exceptionnelle et de l'expérience de production abondante de la Meidensha Corporation. C'est un disjoncteur utilisant des interrupteurs à vide et de l'air sec pour l'isolation. Afin d'éviter l'utilisation de SF6, qui est un gaz à effet de serre, il n'y a aucune crainte de décomposition du gaz due à l'interruption du courant. Il s'agit donc d'un disjoncteur hautement fiable et performant.
Caractéristiques
Disjoncteur de cuve morte optimisé pour les achats verts. Il utilise de l'air sec pour l'isolation à la place du SF6, qui est classé comme un gaz à effet de serre. Notre concept de base de conception est de réaliser les facteurs environnementaux dans la conception (les 3R (Réduire, Réutiliser, Recycler) + LS (Longévité & Séparabilité)) et la réduction des coûts sur le cycle de vie (LCC) comme concepts de base.
Contribution à la prévention du réchauffement climatique
Une isolation à air sec est utilisée au lieu de l'isolation au gaz SF6. Le PGS (Potentiel de Réchauffement Global) du SF6 est de 23 900.
Excellentes performances de coupure
Comme chaque section de coupure de courant utilise un interrupteur à vide, les caractéristiques de récupération de l'isolation sont excellentes. Il présente d'excellentes caractéristiques en cas d'interruption de court-circuit et d'interruption de ligne courte.
Capacité suffisante face aux multiples chocs et aux défauts évolutifs
Comme les intererrupteurs à vide utilisés sont de type auto-diffusion complète de l'arc, ce disjoncteur est le seul capable de gérer les multiples chocs et les courants de défaut évolutifs.
Réduction de la main-d'œuvre pour la maintenance
L'utilisation d'interrupteurs à vide dans les sections de coupure de courant élimine les besoins d'inspection pour ces sections. Par conséquent, les heures de travail peuvent être économisées pour la maintenance et l'inspection.
Type et Caractéristiques
Spécifications
Tension nominale (kV) |
36 |
72,5 |
|
Tension de tenue |
1 min à la fréquence du réseau (kV efficace) |
70 |
140 |
Impulsion 1,2x50μs (kV crête) |
200 |
350 |
|
Fréquence nominale (Hz) |
50/60 |
||
Courant nominal (A) |
2000 |
2000/3150 |
|
Courant de court-circuit nominal (kA) |
31,5 |
40 |
|
Tension de récupération transitoire nominale |
Taux de montée (kV/μs) |
1,19 |
1,47 |
Facteur du premier pôle à éteindre |
1,5 |
||
Courant de fermeture en court-circuit nominal (kA) |
82 |
104 |
|
Courant de court-circuit temporaire nominal (kA) |
31,5 (3s) |
40 (3s) |
|
Temps de coupure nominal (cycle) |
3 |
||
Temps d'ouverture nominal (s) |
0,033 |
0,03 |
|
Temps de fermeture sans charge (s) |
0,05 |
0,10 |
|
Régime de fonctionnement |
O-0,3s-CO-15s-CO |
||
Tension de commande de fermeture (Vdc) |
48, 100, 110, 125, 250 |
||
Tension nominale de déclenchement (Vdc) |
48, 100, 110, 125, 250 |
||
Tension d'alimentation pour le moteur de charge |
(Vdc) |
48, 100, 110, 125, 250 |
|
(Vac) |
60, 120, 240 |
||
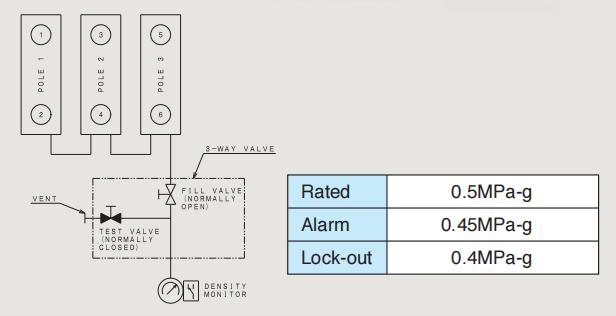
Pression nominale d'air sec |
0,5MPa-g (à 20℃ ) |
||
Système de commande de fermeture |
ressort |
||
Système de commande de déclenchement |
ressort |
||
Norme applicable |
IEC 62271-100-2008, ANSI/IEEE C37.06-2009 |
||
Construction
Structure générale
Pour chaque phase, un disjoncteur à vide interrompant le courant est logé dans la cuve mise à la terre. Le système d'exploitation est conçu de telle manière que la fermeture et l'ouverture sont effectuées par force de ressort. Le mécanisme de commande et le couplage triphasé sont assemblés sur une base commune, qui est installée sur les pieds du cadre.
Structure interne
La structure globale est principalement composée de la cuve mise à la terre, des disjoncteurs à vide (VI), des tiges isolantes, des embases et des bornes de circuit principal. Chaque cuve mise à la terre est remplie d'air sec maintenu à une pression nominale de 0,5 MPa-g (20°C).
Structure interne du disjoncteur à vide
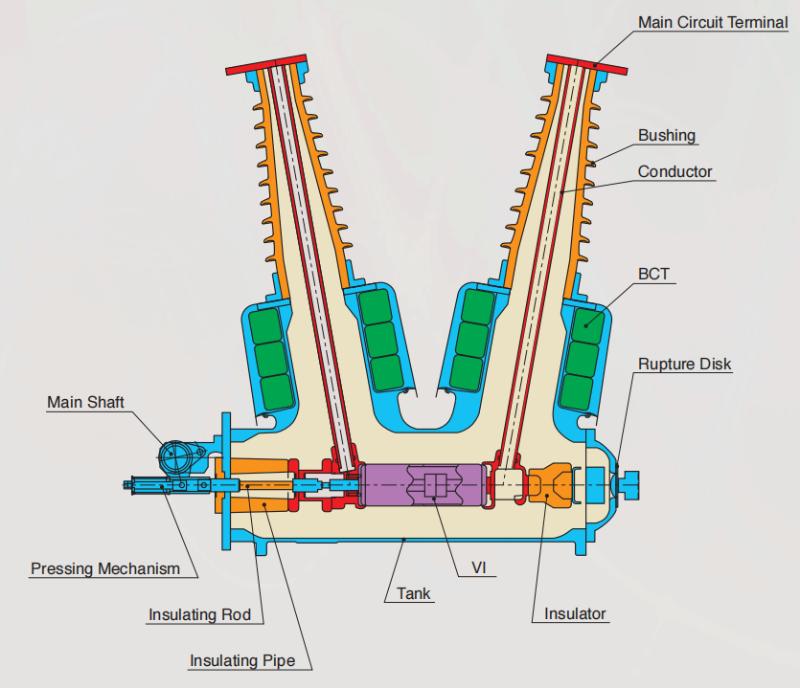
Système d'air sec
Dessin d'ensemble
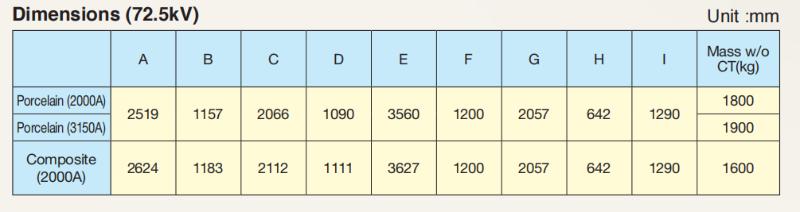
Dimensions (72,5 kV)
Dimensions (36 kV)
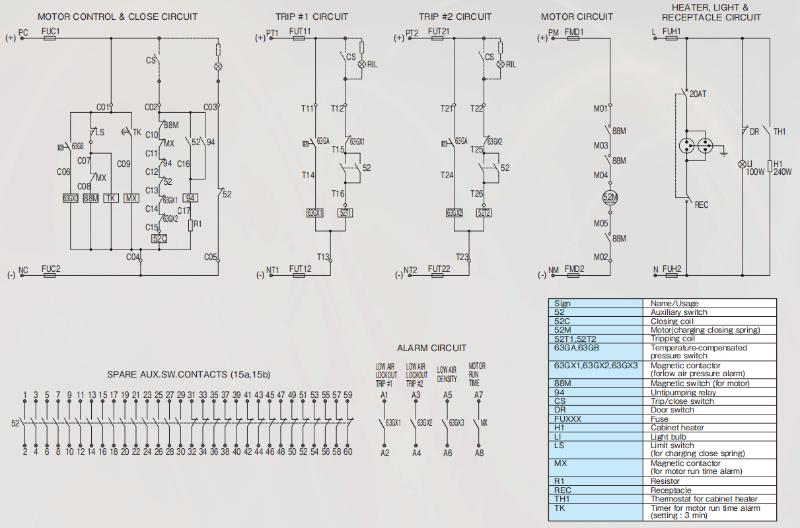
Diagramme de connexion standard
Performance
Les performances du disjoncteur ont été conçues conformément aux normes ANSI et IEC, et vérifiées par des essais de type. Tous les produits sont expédiés après confirmation de diverses performances par des essais d'acceptation basés sur ces normes.
Caractéristiques de tenue en tension : Les performances de tenue en tension sont garanties à la pression d'air sec spécifiée. Même si la pression d'air sec est réduite au niveau d'alarme, le niveau d'isolation requis peut être assuré. De plus, même si cette pression baisse à la pression atmosphérique, le disjoncteur résiste à la tension nominale.
Performance de passage de courant : Comme les contacts principaux sont situés sous vide, leurs surfaces ne s'oxydent jamais et la performance de passage de courant est donc stabilisée. En mode de fermeture du disjoncteur, une force de pression est exercée entre les contacts principaux grâce à l'effet du ressort de pression, ce qui assure une tolérance suffisante contre le courant de fermeture et le courant de courte durée.
Vie mécanique : Grâce à l'adoption d'un mécanisme de fonctionnement simplifié, les caractéristiques de commutation sont extrêmement stabilisées. La performance de commutation fréquente a également été vérifiée par des essais de commutation mécanique continue en répétant les opérations de commutation plus de 10 000 fois.
Vie électrique : Comme l'interruption du courant est effectuée dans l'interrupteur à vide, l'énergie d'arc générée lors de l'interruption du courant est extrêmement faible et l'érosion des contacts est minimale. Cela implique une longue durée de vie des contacts. Commutation de courant de charge : 10 000 fois
Commutation de courant nominal d'interruption : 20 fois

Structure intégrale du réservoir:
-
Structure intégrale du réservoir : La chambre d'extinction d'arc, le milieu isolant et les composants associés sont scellés dans un réservoir métallique rempli de gaz isolant (comme l'hexafluorure de soufre) ou d'huile isolante. Cela forme un espace relativement indépendant et scellé, empêchant efficacement les facteurs environnementaux externes d'affecter les composants internes. Cette conception améliore les performances d'isolation et la fiabilité de l'équipement, le rendant adapté à divers environnements extérieurs difficiles.
Disposition de la chambre d'extinction d'arc:
-
Disposition de la chambre d'extinction d'arc : La chambre d'extinction d'arc est généralement installée à l'intérieur du réservoir. Sa structure est conçue pour être compacte, permettant une extinction d'arc efficace dans un espace limité. En fonction des principes et technologies d'extinction d'arc différents, la construction spécifique de la chambre d'extinction d'arc peut varier, mais elle comprend généralement des composants clés tels que les contacts, les buses et les matériaux isolants. Ces composants travaillent ensemble pour s'assurer que l'arc est rapidement et efficacement éteint lorsque l'interrupteur interrompt le courant.
Mécanisme d'exploitation:
-
Mécanisme d'exploitation : Les mécanismes d'exploitation courants incluent les mécanismes à ressort et les mécanismes hydrauliques.
-
Mécanisme à ressort : Ce type de mécanisme est simple en structure, très fiable et facile à entretenir. Il entraîne les opérations d'ouverture et de fermeture de l'interrupteur par le stockage et la libération de l'énergie des ressorts.
-
Mécanisme hydraulique : Ce mécanisme offre des avantages tels qu'une puissance de sortie élevée et une opération fluide, ce qui le rend adapté aux interrupteurs de classe haute tension et haute intensité.






















