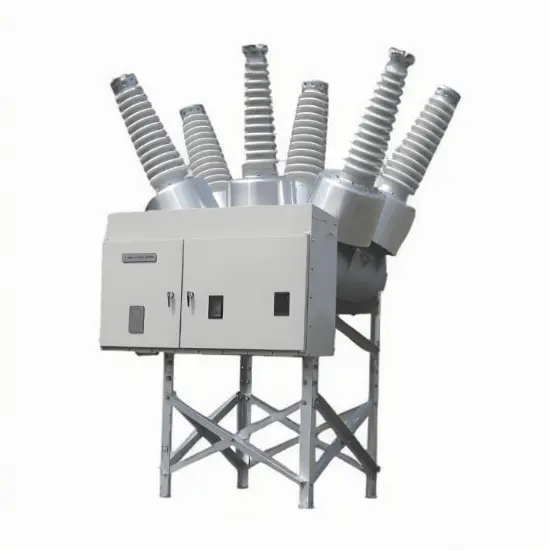
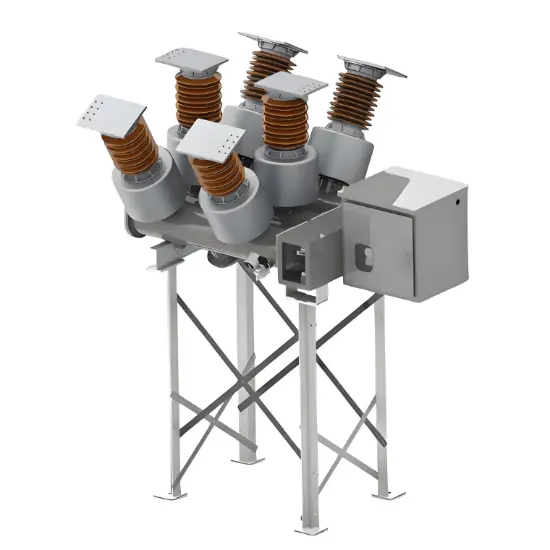
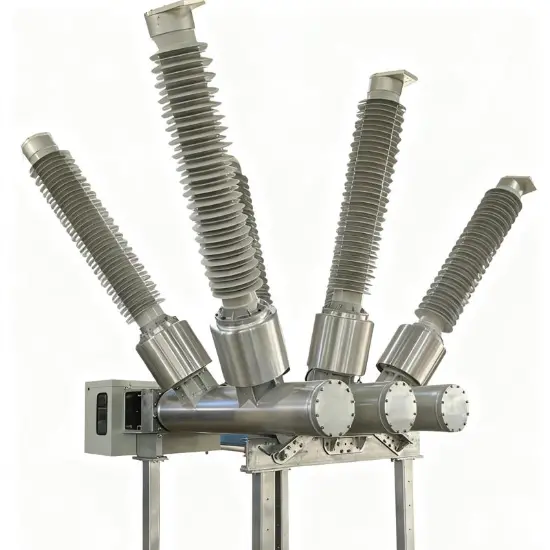
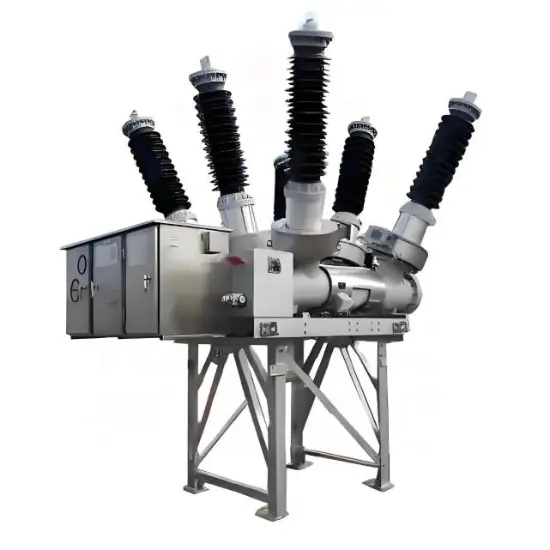
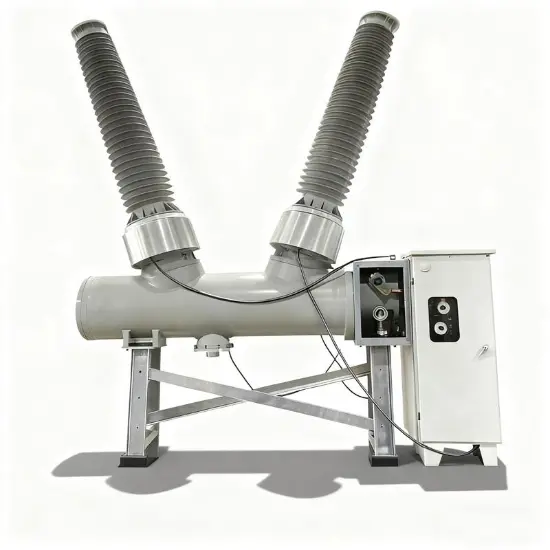
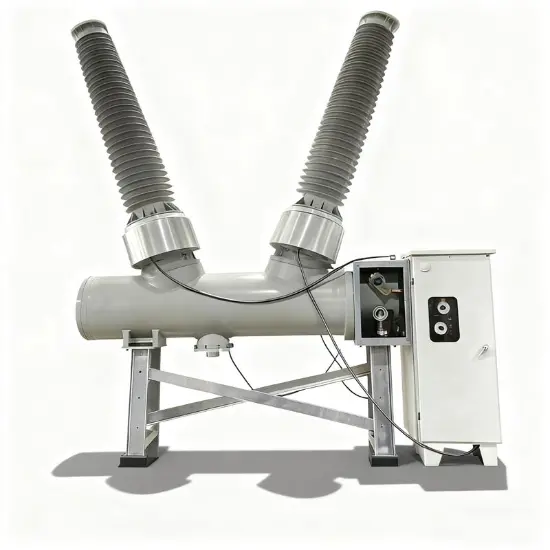
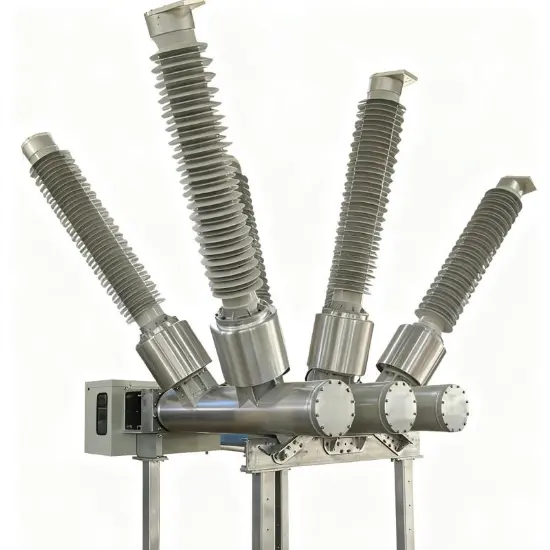
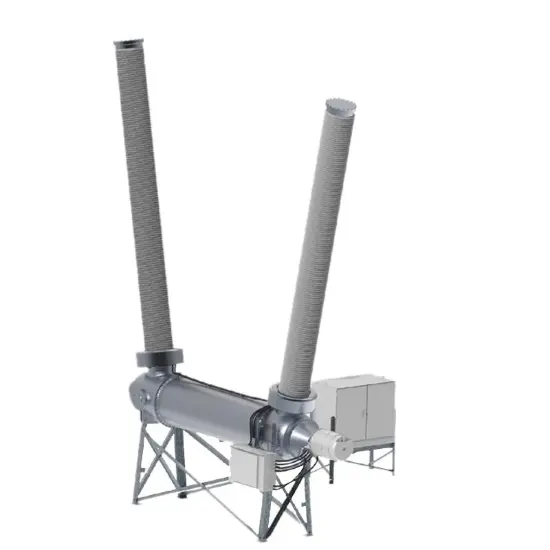
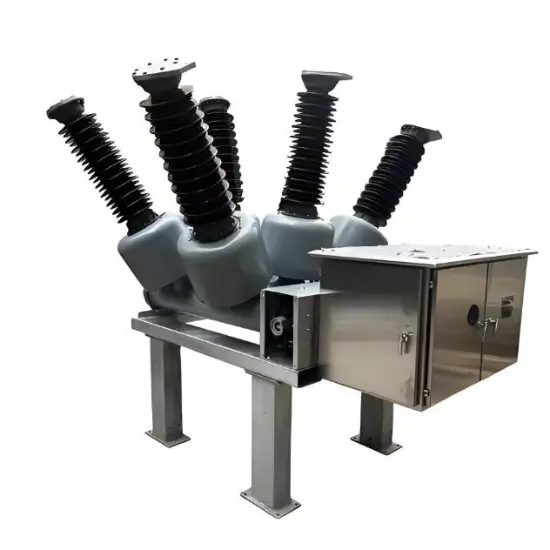
36kV 72.5kV Interruptor de Vácuo com Isolamento a Ar Seco e Tanque Morto (VCB)
| Marca | ROCKWILL |
| Número do Modelo | 36kV 72.5kV Dry Air Insulated Dead Tank Vacuum Circuit Breaker(VCB) |
| Tensão nominal | 72.5kV |
| Corrente nominal | 2000A |
| Frequência nominal | 50/60Hz |
| Série | NVBOA |
Descrição
O Disjuntor de Tanque Morto Isolado a Ar Seco nasceu da tecnologia superior e da vasta experiência de produção da Meidensha Corporation. É um disjuntor que utiliza interrompedores a vácuo e ar seco para isolamento. Para não usar SF6, que é um gás de efeito estufa, não há risco de decomposição do gás devido à interrupção de corrente. Portanto, é um disjuntor altamente confiável e de alto desempenho.
Características
Disjuntor de Tanque Morto VCB otimizado para aquisição verde. Utiliza ar seco para isolamento em vez do SF6, que é especificado como gás de efeito estufa. Nosso conceito básico de design é realizar os fatores ambientais no design (os 3Rs (Reduzir, Reutilizar e Reciclar) + LS (Longa duração & Separável)) e a redução do custo total ao longo da vida útil (LCC) como conceitos básicos.
Contribuição para a prevenção do aquecimento global
É empregado o isolamento a ar seco em vez do isolamento com gás SF6. O PGE (Potencial de Aquecimento Global) do SF6 é 23.900.
Excelente desempenho de interrupção
Como cada seção de interrupção de corrente utiliza um interrompedor a vácuo, as características de recuperação de isolamento são excelentes. Ele exibe características superiores em casos de interrupção de curto-circuito e interrupção de falhas em linhas curtas.
Capacidade suficiente contra múltiplos descargas e falhas evolutivas
Como os interrompedores a vácuo utilizados são do tipo totalmente auto-difusão de arco, este disjuntor é a única unidade capaz de lidar com múltiplas descargas e correntes de falha evolutivas.
Redução de trabalho de manutenção
O uso de interrompedores a vácuo nas seções de interrupção de corrente elimina a necessidade de inspeção dessas seções. Portanto, horas-homem podem ser economizadas para manutenção e inspeção.
Tipo e Especificações
Especificações
Tensão nominal (kV) |
36 |
72.5 |
|
Tensão de resistência |
1 min frequência de rede (kV eficaz) |
70 |
140 |
Impulso 1.2x50μs (kV pico) |
200 |
350 |
|
Frequência nominal (Hz) |
50/60 |
||
Corrente nominal (A) |
2000 |
2000/3150 |
|
Corrente de curto-circuito nominal do disjuntor (kA) |
31.5 |
40 |
|
Tensão de recuperação transitória nominal |
Taxa de subida (kV/μs) |
1.19 |
1.47 |
Fator do primeiro polo a desligar |
1.5 |
||
Corrente de fechamento em curto-circuito nominal (kA) |
82 |
104 |
|
Corrente de tempo curto nominal (kA) |
31.5 (3s) |
40 (3s) |
|
Tempo de interrupção nominal (ciclos) |
3 |
||
Tempo de abertura nominal (s) |
0.033 |
0.03 |
|
Tempo de fechamento sem carga (s) |
0.05 |
0.10 |
|
Ciclo de operação |
O-0.3s-CO-15s-CO |
||
Tensão de comando de fechamento (Vdc) |
48, 100, 110, 125, 250 |
||
Tensão de comando de desligamento nominal (Vdc) |
48, 100, 110, 125, 250 |
||
Tensão de alimentação para motor de carregamento |
(Vdc) |
48, 100, 110, 125, 250 |
|
(Vac) |
60, 120, 240 |
||
Pressão nominal de ar seco |
0.5MPa-g (a 20℃ ) |
||
Sistema de operação de fechamento |
Mola |
||
Sistema de controle de desligamento |
Mola |
||
Padrão aplicável |
IEC 62271-100-2008, ANSI/IEEE C37.06-2009 |
||
Construção
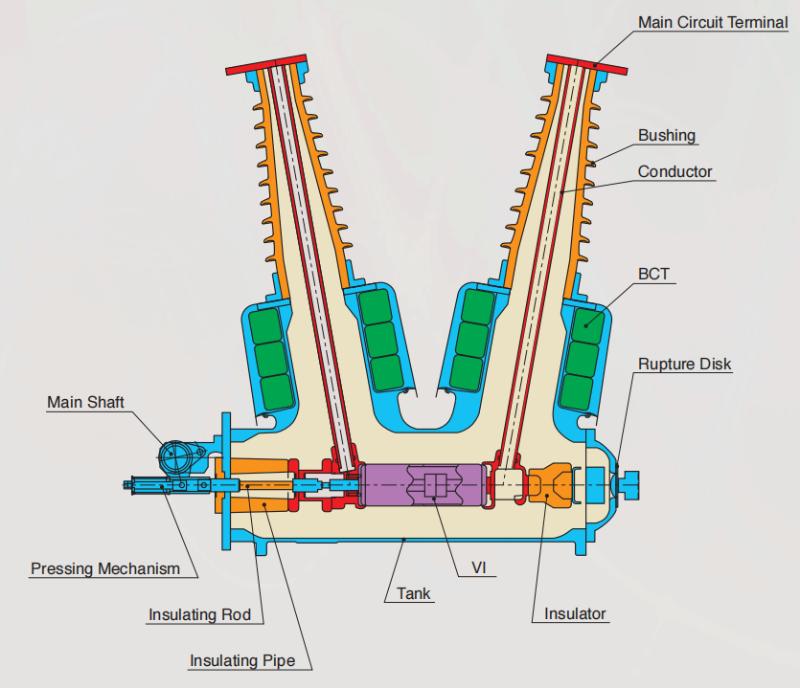
Construção geral
Para cada fase, um interrompedor de vácuo para quebra de corrente é acomodado no tanque aterrado. O sistema de operação é tal que o fechamento e a abertura são realizados por força de mola. O mecanismo de operação e a interligação trifásica são montados em uma base comum, que é instalada nas pernas do quadro.
Construção interna
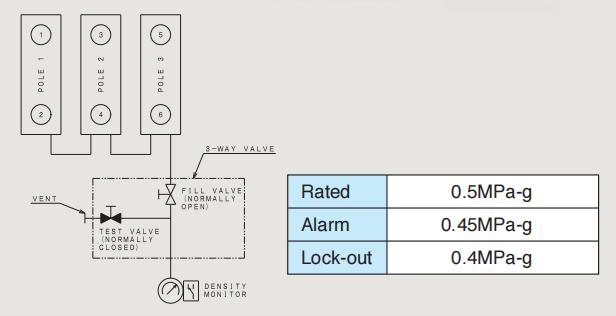
A estrutura geral é composta principalmente pelo tanque aterrado, interrompedores de vácuo (IV), varas isolantes, bushings e terminais de circuito principal. Cada tanque aterrado é preenchido com ar seco mantido sob pressão nominal de 0,5 MPa-g (20℃).
Construção interna do disjuntor de vácuo
Sistema de ar seco
Desenho de esquema
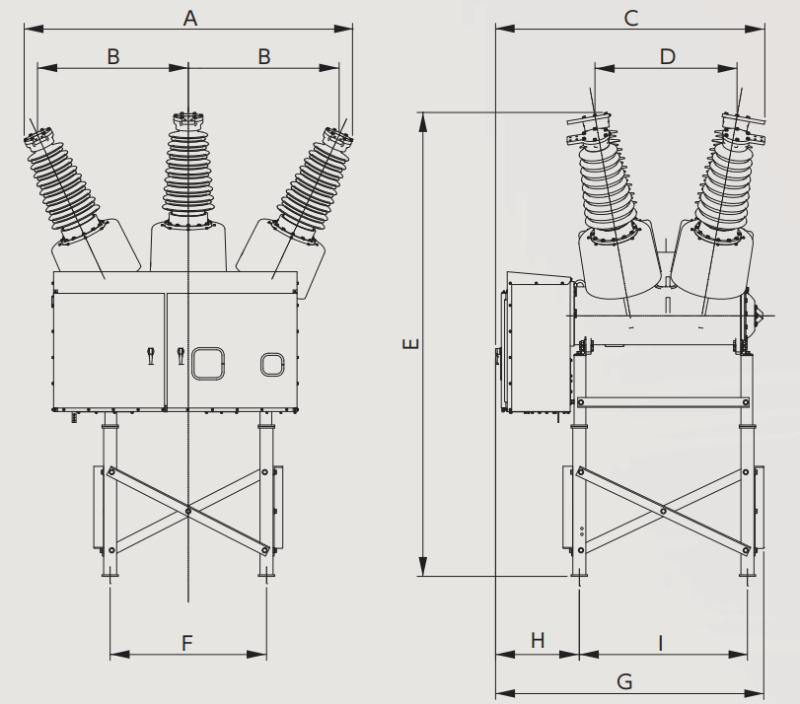
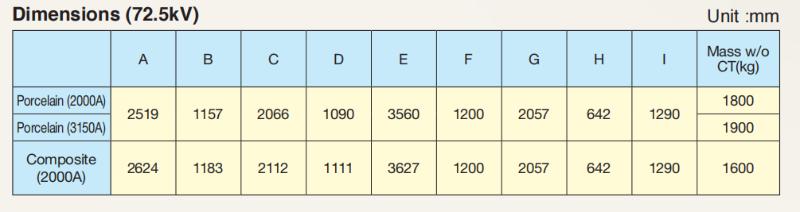
Dimensões (72,5 kV)
Dimensões (36 kV)
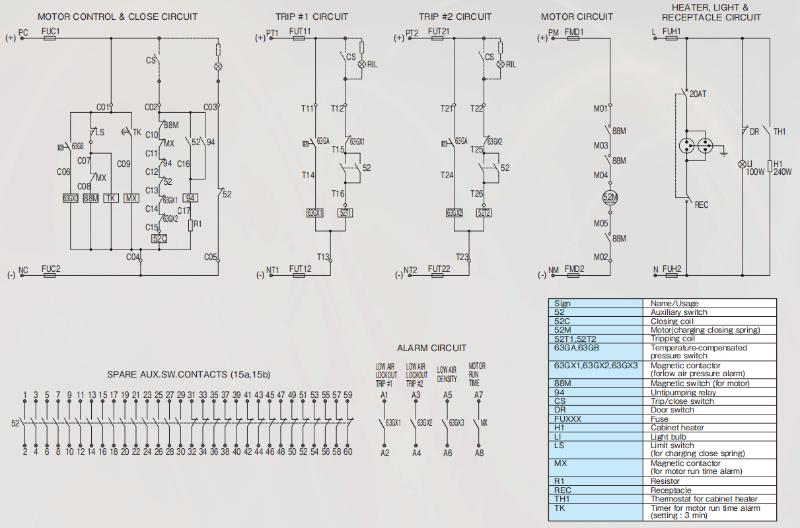
Diagrama de conexão padrão
Desempenho
O desempenho do disjuntor foi projetado de acordo com os padrões ANSI e IEC e verificado através de testes de tipo. Todos os produtos são enviados após a confirmação de vários desempenhos por meio de testes de aceitação baseados nesses padrões.
Características de resistência à tensão : O desempenho de resistência à tensão está assegurado na pressão especificada de ar seco. Mesmo que a pressão de ar seco tenha sido reduzida para o nível de alarme, o nível de isolamento necessário pode ser assegurado. Além disso, mesmo que esta pressão seja reduzida para a pressão atmosférica, o disjuntor resiste à tensão nominal.
Desempenho de passagem de corrente : Como os contatos principais estão localizados sob vácuo, suas superfícies nunca são oxidadas e, portanto, o desempenho de passagem de corrente é estabilizado. No modo de fechamento do disjuntor, uma força de compressão é exercida entre os contatos principais pelo efeito da mola de compressão, assegurando tolerância suficiente contra a corrente de fechamento e a corrente de curto prazo.
Vida útil mecânica : Devido à adoção de um mecanismo de operação simplificado, as características de comutação são extremamente estabilizadas. O desempenho de comutação frequente também foi verificado através de testes de comutação mecânicos contínuos, repetindo as operações de comutação mais de 10.000 vezes.
Vida útil elétrica : Como a interrupção de corrente é realizada no interrompedor de vácuo, a energia gerada durante a interrupção de corrente é extremamente baixa e a erosão dos contatos é mínima. Isso implica em longa vida útil dos contatos. Comutação de corrente de carga: 10.000 vezes
Comutação de corrente nominal de interrupção: 20 vezes

Estrutura do Tanque Integral:
-
Estrutura do Tanque Integral: A câmara de extinção de arco, o meio isolante e os componentes relacionados estão selados dentro de um tanque metálico preenchido com gás isolante (como hexafluoreto de enxofre) ou óleo isolante. Isso forma um espaço relativamente independente e selado, efetivamente impedindo que fatores ambientais externos afetem os componentes internos. Este design aumenta o desempenho de isolamento e a confiabilidade do equipamento, tornando-o adequado para vários ambientes externos adversos.
Disposição da Câmara de Extinção de Arco:
-
Disposição da Câmara de Extinção de Arco: A câmara de extinção de arco geralmente é instalada dentro do tanque. Sua estrutura é projetada para ser compacta, permitindo uma extinção de arco eficiente em um espaço limitado. Dependendo dos diferentes princípios e tecnologias de extinção de arco, a construção específica da câmara de extinção de arco pode variar, mas geralmente inclui componentes-chave como contatos, bocais e materiais isolantes. Esses componentes trabalham juntos para garantir que o arco seja rapidamente e efetivamente extinto quando o disjuntor interrompe a corrente.
Mecanismo de Operação:
-
Mecanismo de Operação: Mecanismos de operação comuns incluem mecanismos acionados por mola e mecanismos acionados hidraulicamente.
-
Mecanismo Acionado por Mola: Este tipo de mecanismo tem uma estrutura simples, é altamente confiável e fácil de manter. Ele impulsiona as operações de abertura e fechamento do disjuntor através do armazenamento e liberação de energia das molas.
-
Mecanismo Acionado Hidraulicamente: Este mecanismo oferece vantagens como alta potência de saída e operação suave, tornando-o adequado para disjuntores de classe de alta tensão e alta corrente.






















